
1. The photo on the left shows 2 urea broth tubes that were inoculated with different bacteria.
A. Which of these 2 tubes contains urease-positive bacteria?
B. Give one example of how urease can be helpful to bacteria.
C. What are the breakdown products of urea?
D. Is the urease-positive broth more acidic or alkaline than the control?

2. The photo on the left shows 2 citrate slants that were inoculated with different bacteria.
A. Which of these 2 slants contains bacteria that can use citrate?
B. What do bacteria use citrate for?
C. What metabolic pathway is citrate used in?
D. Is the citrate-positive slant more acidic or alkaline than the control?
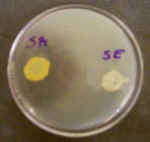
3. The DNAse plate on the left was incubated with 2 bacteria and then treated with HCl.
A. Which of these 2 bacteria is DNAse-positive?
B. When DNA is broken down, what monomers are produced?
C. Which of these 2 bacteria is likely to be more pathogenic?
D. Why was hydrochloric acid (HCl) added?
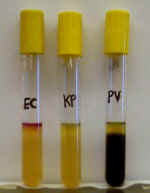
4. Examine the SIM deeps pictured on the left.
A. Which of these deeps displays indole production?
B. Which of these deeps displays H2S production?
C. Name the 2 sources of H2S in bacterial metabolism.
D. Where does indole come from?
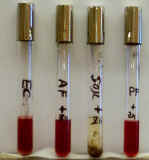
5. Examine these nitrate broths. (The tubes labeled "+Zn" had no color change before zinc was added).
A. Which of the 4 tubes shown on the left show evidence of bacterial nitrate reduction?
B. Which of these 4 tubes shows evidence of denitrification?
C. What can nitrate be reduced to?
D. During what metabolic process does this occur?
6. For the 3 Gelatin deeps pictured on the left:
A. Which of these 3 tubes contain(s) gelatinase-positive bacteria?
B. What is gelatin broken down into?
C. How can this enzyme help bacteria?

7. For the glucose fermentation tube seen on the left:
A. What type of fermentation (Base, negative, acid, gas) occurred?
B. Give some specific examples of fermentation products that can account for this.
C. What sugar(s) can this bacterium ferment?
D. The ph of this medium is ___________.
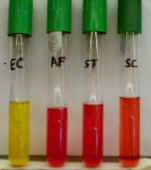
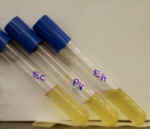
8. For the 4 lactose fermentation tubes shown here:
A. Which of these bacteria is/are able to ferment lactose?
B. What causes the color in the tube marked "AF"?
C. Which of these organisms shows a neutral reaction?
D. What enzyme does EC have that the other 3 organisms don't?

9. For the starch agar plate shown here:
A. Which of these 3 organisms can break down starch?
B. What enzyme is needed to break down starch?
C. What causes the blue coloring in the agar?
D. What is the major breakdown product?

10. For the motility deeps shown here:
A. Which of these 3 organisms is/are motile?
B. What part of the cell is necessary for motility?
C. What other culture medium can be used to determine motility?
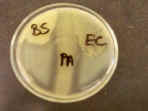
11. For the milk agar plate shown here:
A. Which of these 3 organisms can break down milk protein?
B. What is the name of this protein?
C. What is the protein broken down into?
D. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down this protein?

12. For the Methyl Red test seen here:
A. Which of these 2 tubes shows a positive test?
B. What type of fermentation do MR+ bacteria carry out?
C. What is the pH of these 2 tubes?
D. Name some specific fermentation products you might find in the positive tube.

13. For the two MRVP broths shown here (30 minutes after adding Barritt's reagent):
A. What is this test called?
B. Which of these 2 tubes shows a positive test result?
C. What fermentation pathway can this test detect?
D. How is this test related to the Methyl Red test?