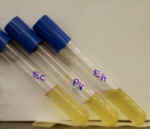
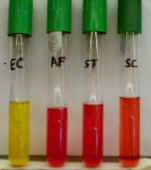
1. The photo on the left shows 2 urea broth tubes that were inoculated with different bacteria.
A. Which of these 2 tubes contains urease-positive bacteria?
The tube on the right - dark red color
B. Give one example of how urease can be helpful to bacteria.
1. Survival in acidic environments; 2. To obtain nitrogen.
C. What are the breakdown products of urea?
Carbon dioxide and ammonium
D. Is the urease-positive broth more acidic or alkaline than the control?
The dark red color indicates alkaline reaction (due to ammonium)

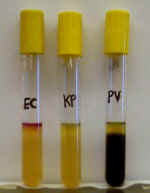
2. The photo on the left shows 2 citrate slants that were inoculated with different bacteria.
A. Which of these 2 slants contains bacteria that can use citrate?
The tube on the left - blue color
B. What do bacteria use citrate for?
As a carbon/energy source
C. What metabolic pathway is citrate used in?
The Krebs cycle
D. Is the citrate-positive slant more acidic or alkaline than the control?
The blue color indicates an alkaline reaction due to removal of citric acid and formation of sodium carbonate (due to the carbon dioxide)