Tour of Microbes Tour Home | Disease Home | Microbes A to Z | Bio 203 Home |

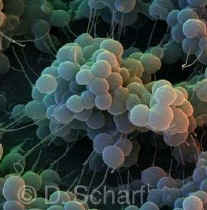

Staphylococcus cluster
Staphylococcus (EM)
Staphylococcus aureus colonies
Staphylococcus is a catalase-positive Gram-positive coccus that is normally arranged in clusters. It is a facultatively anaerobic chemoheterotroph commonly found on skin and mucous membranes. Important species in this genus include S. aureus (an opportunistic pathogen) and S. epidermidis. Staphylococci are salt-tolerant. S. aureus is a frequent concern in hospitals due to its ability to produce virulence factors such as DNAse, gelatinase, and coagulase, and due to the appearance of methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA).
Domain Bacteria
Phylum Firmicutes
Class Bacilli
Bergey's Manual Volume 3: The low G+C Gram-positive Bacteria
Facultative anaerobe, oxidase-negative, catalase-positive, nitrate reduction-positive
Metabolism: respiratory and fermentative (Acid from glucose, lactose, sucrose),
Hydrolysis: amylase-negative, DNAse-positive, casease-positive
Other: H2S-negative, indole-negative, citrate-negative, urease-positive, coagulase-positive
Structure: non-motile
Same as above except: DNAse-negative, casease-negative, nitrate-negative, coagulase-negative