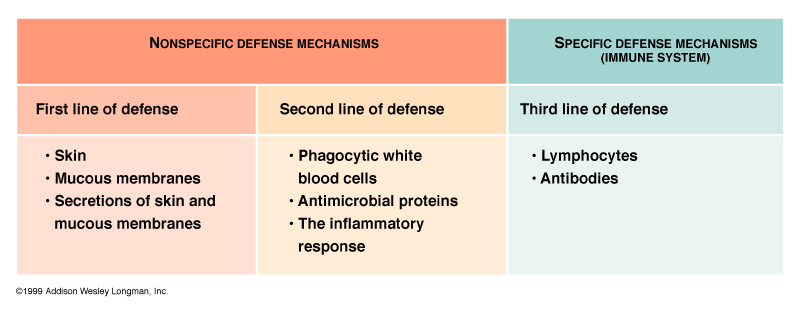


Differentiation of immune system cells
Resident B cells, T cells, dendritic cells
Antigen response: proliferation & swelling
Homing receptors (addressins) for B & T cells
Phagocytes respond to chemoattractant mediators, e.g. C5a
My Home | Course Home | Plattsburgh Home | Biological Sciences