Physical Defense - barriers
-
Skin (keratinized stratified epithelium)
-
Mucous membranes (mucus)
Mechanical Defense - movements
-
Mucociliary action
-
Peristalsis
-
Chewing (mastication)
-
GI motility (grinding, peristalsis)
-
Fluid movement (urine, GI tract, mouth)
-
Shedding of epithelium
Biochemical Defense - secretions
-
Lysozyme (tears, skin, saliva)
-
Organic acids (skin, vagina)
-
Hydrochloric acid (stomach)
-
Bile (intestine)
-
IgA (intestine, breast milk, saliva)
-
Mucus
-
Defensins/Antimicrobial peptides (lungs, urine)
-
Digestive enzymes (stomach, intestines)
-
Iron-binding proteins: lactoferrin
-
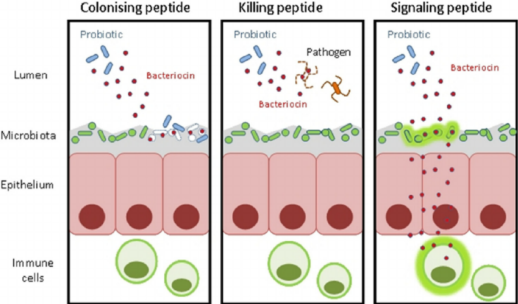
Bacteriocins - normal microbiota