Streptococcal infections 
Introduction.
Streptococci are part of the normal human microbiota and occur in a variety
of serotypes. Some of these are clearly pathogenic, while others are
opportunistic.
Depending on the virulence factors present and the serotype, Strep
infections can range from Strep throat to toxic shock syndrome.
Group A Streptococcus: S. pyogenes
- beta hemolysis and bacitracin-sensitive on blood agar
- Multiple virulence factors include:
- M-protein (adhesion, antiphagocytic)
- F-protein (adhesion, internalization)
- Capsule
- Pyrogenic exotoxins (Spe) - superantigens

- Streptolysins (hemolysis, leukocidal)
- Streptokinase: lyses blood clots
- DNAse, C5a peptidase
Pharyngitis (Strep throat)
- Sore throat, fever, malaise, headache
- Easily confused with viral causes
Scarlet fever
- Complication of pharyngitis due to lysogenic bacteriophage
- Diffuse red rash except palms, soles & around mouth; strawberry tongue
- Pyrogenic exotoxin (Spe) produces the rash

Pyoderma (impetigo)
- Pus-filled vesicles; little systemic involvement
- Exposed skin areas (legs, arms)
Erysipelas
- Local inflammation and systemic signs (fever, chills)
- Outer skin layers very red and raised
Cellulitis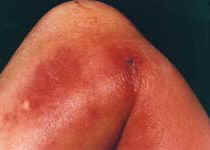
- Deeper skin layers infected
- Redness, less distinct rash, systemic signs
Necrotizing fasciitis
- Deep tissue involvement;
bacteria multiply in muscle and fat
- Tissue necrosis common; rapid spread must be stopped with tissue
debridement
- Systemic signs, shock and death (50% mortality)
Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Inflammation at site of infection

- Systemic bacteremia, fever, chills, nausea, malaise
- Often associated with NF
- Mortality common due to shock (Spe toxins)
Rheumatic fever
- Inflammation of heart, blood vessels, joints
- Often associated with strep throat (not with skin infections)
Acute glomerulonephritis
- Inflammation of kidneys: edema, hypertension, blood & protein in urine
Group B Streptococcus: S. agalacticae
- beta-hemolytic and positive for the CAMP test
-
Puerperal fever: sepsis
- Neonatal disease (bacteremia, pneumonia, meningitis)
Viridans Streptococci
- alpha hemolytic; fastidious; many species
- Dental caries (S. mutans)
- Endocarditis
S. pneumoniae
- alpha hemolysis; sensitive to optochin
- Gram-positive diplococci with capsule
- Produce virulence factors: adhesins, IgA protease, pneumolysins (damage
ciliated epithelial cells)
- Cause inflammation at site of infection leading to edema
- Pneumococcal pneumonia (5% mortality)
- Complications include bacteremia, which can lead to pneumococcal meningitis





