![]()
Biology 202 - Introduction to Microbiology
|
|
Biology 202 - Introduction to Microbiology |
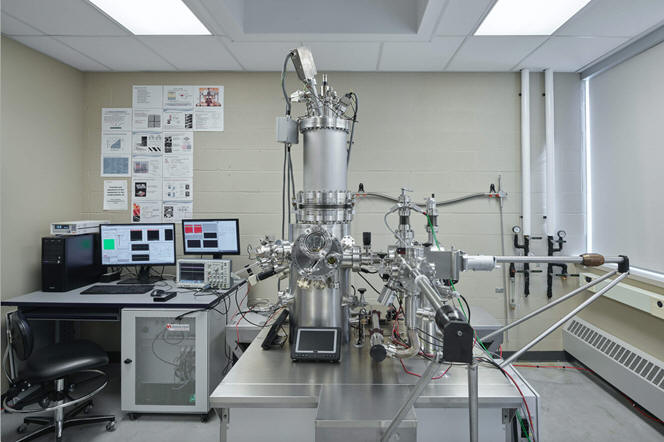
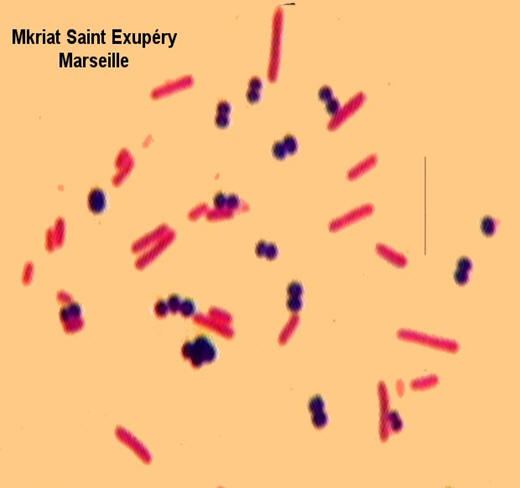


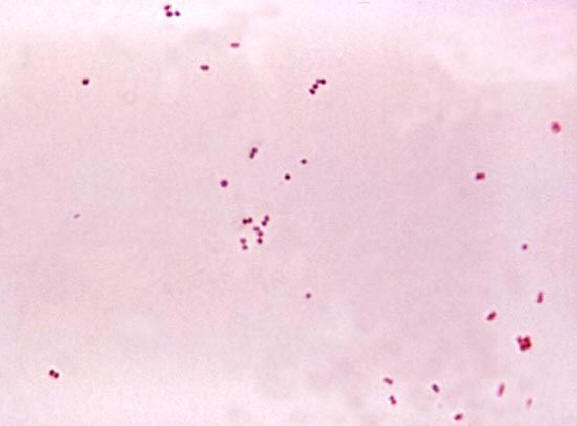
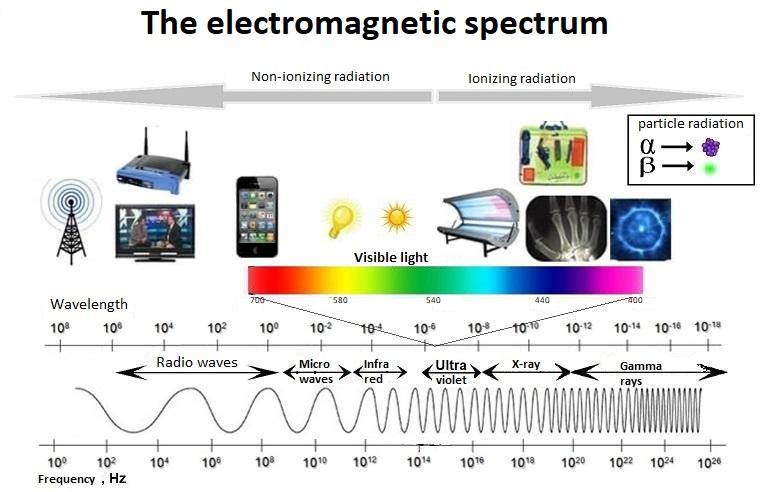
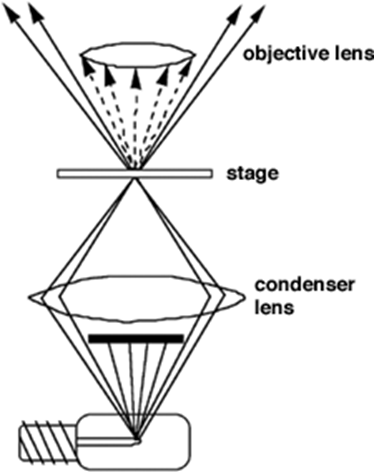
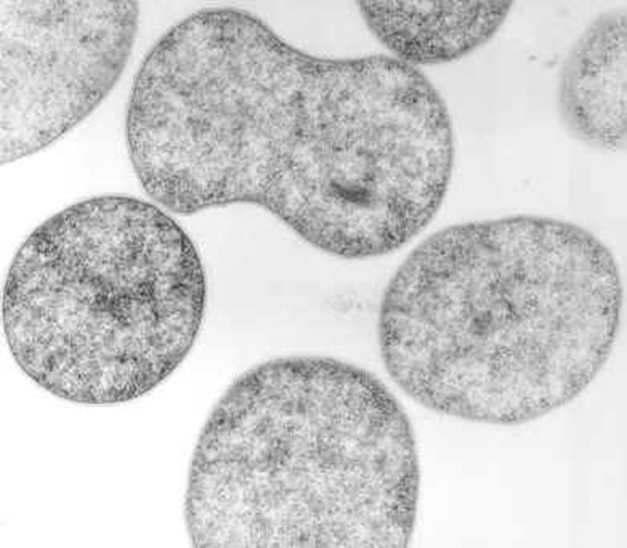

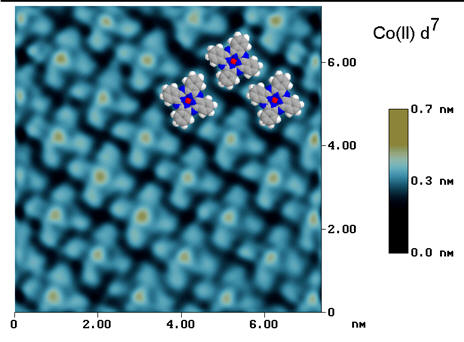

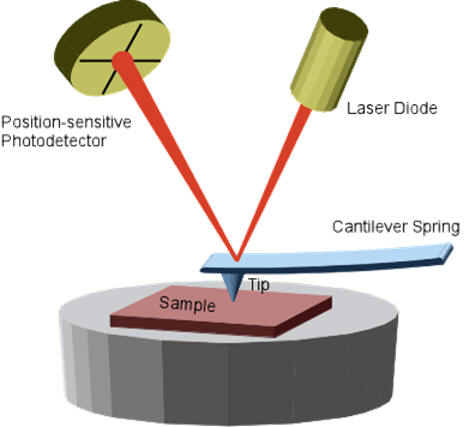


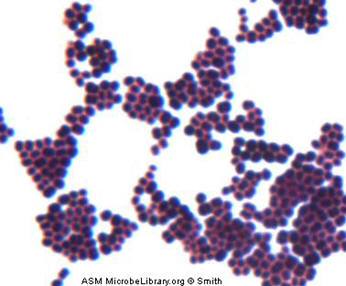

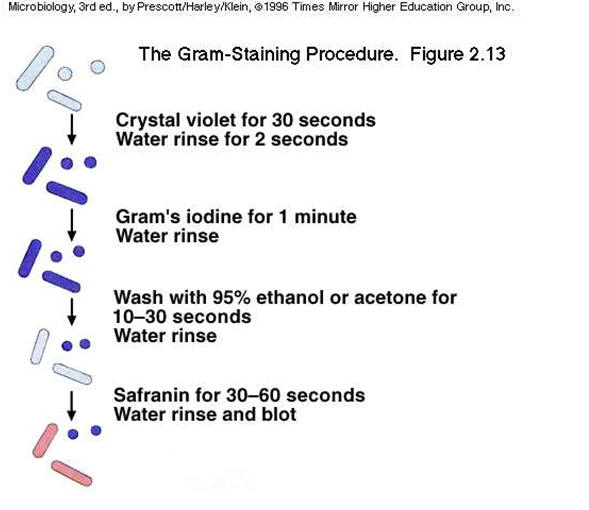

SUNY Plattsburgh | Department of Biological Sciences | Medical Technology | Cytotechnology | My Research Interests
© 2000 - 2023 Josť de Ondarza - Contact jose.deondarza@plattsburgh.edu