Reproduction & Development
Reprise: What is LIFE?
A. Modes of reproduction
- Asexual reproduction - lower invertebrates
- Fission
- Budding
- Fragmentation & regeneration
- Hermaphroditism
- e.g. earthworms, sponges
- Sequential hermaphroditism - some fish
- External fertilization
- Aquatic invertebrates, amphibians, fish
- Large number of offspring
- Moist environment
- Internal fertilization
- Development of embryo
- Oviparous: within an egg
- Viviparous: live birth
B. Male reproductive system
- Penis
- Urethra
- Erectile tissue
- Scrotum
Internal genitalia
- Testes
- Seminiferous tubules: Spermatogenesis
- Spermatocytes go thru meiosis I
- Spermatids go thru meiosis II
- Sperm cells mature: flagella, acrosome
- Leydig cells
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Sperm storage & ejaculation
- Seminal vesicles
- Nutrient-rich fluid (fructose)
- Prostate gland
- Adds 'alkaline' fluid (pH ~ 6.5)
- Bulbourethral gland
C. Female reproductive system
- Labia majora & minora
- Clitoris
Internal genitalia
- Vagina
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Endometrium
- Myometrium (smooth muscle)
- Oviducts (Fallopian tubes)
- Ovaries: oogenesis
- Oocytes (stuck in prophase I of meiosis)
- Follicles (400,000 are left at puberty)
- stimulated to grow by FSH
- only one follicle matures per month (Graafian follicle)
- Corpus luteum
- LH causes ovulation
- Remaining cells of follicle become corpus luteum
D. The female reproductive cycle
- The ovarian cycle
- Follicular phase: FSH stimulates growth of follicle
- Ovulation: LH surge causes rupture of follicle
- Luteal phase: LH causes corpus luteum to secrete Estrogen +
Progesterone
- The menstrual cycle
- Menstrual phase: Lack of E+P = uterine lining shed
- Proliferative phase: Rise in Estrogen causes growth of uterine
lining
- Secretory phase: Rise in Progesterone causes thickening/secretion of
lining

E. Pregnancy
- Fertilization
- Sperm penetration (only 1 sperm allowed)
- egg & sperm nuclei fuse = zygote
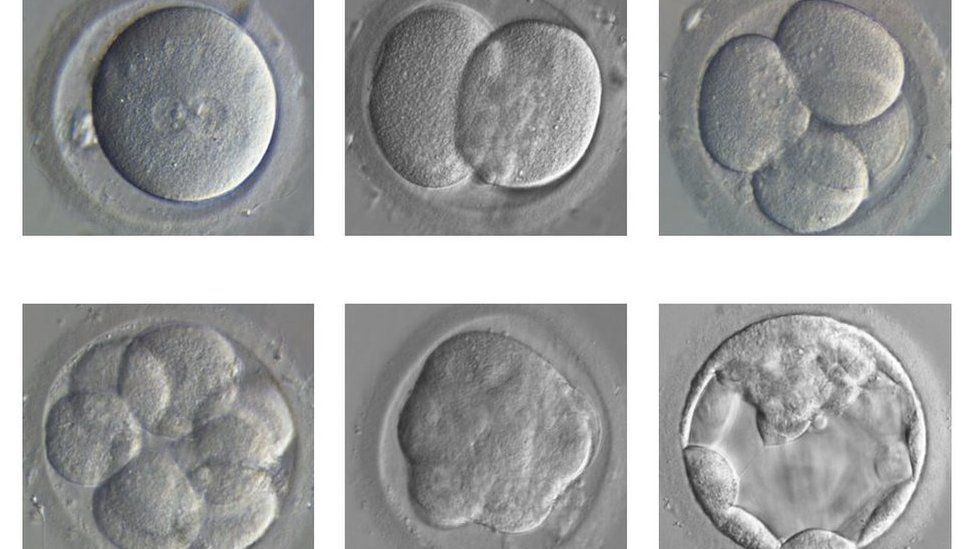
- Implantation
- Blastocyst (~ 16 cells) reaches endometrium
- Trophoblast (outer layer of cells) becomes placenta
- produces hCG (detectable by day 6)
- Embryonic growth
- Gastrulation
- Ectoderm becomes nervous system + epidermis
- Endoderm: Linings of intestinal tract, liver, pancreas
- Mesoderm: internal organs (heart, kidney)
Mother & fetus are 2 genetically distinct individuals,
creating the possibility of immune system reactions. For example, erythroblastosis fetalis
(Rh factor incompatibility) can be a
problem.
-
 Neural
tube forms ~ 1 week-old
Neural
tube forms ~ 1 week-old
- Rapid differentiation of CNS ~2 week-old
- Fetal heartbeat begins ~ 3 week-old
- Mouth & eyes; muscles & movement ~ 5
week-old
- Brainwaves present, arms/legs/fingers ~ 6 week-old
- Heart almost complete; AV shunt ~ 8 week-old
- Brain fully formed; pain sensation present ~ 10 week-old
- Taste buds present ~ 13 week-old
- Eyebrows, eyelashes, hair;
grasping, kicking movements ~ 14 week-old
- Child can suck thumb! see photo here >>>>>>>
- Gender easily seen; fingernails & fingerprints ~ 18 week-old
- Lungs develop; fetus 'inhales' amniotic fluid ~ 22 week-old
- I can stick my tongue out! ~ 24
weeks
- Indications of REM sleep present ~ 30 week-old
- Labor
- Oxytocin & prostaglandins
Application topics
- STDs
- Contraception
- In vitro fertilization
- Infertility

 Neural
tube forms ~ 1 week-old
Neural
tube forms ~ 1 week-old