Physiology: An Overview
Structure & Function of animals
"Form Fits Function"
- Cells
- Form Fits Function!
- Squamous and cuboidal epithelial cells
- Sensory neurons & interneurons
- Tissues
- Epithelial
tissue
- Layer(s) of connected cells
- Control passage of chemicals, water, and cells
- Epidermis & Internal linings of organs
- Connective
tissue
- Cells imbedded in matrix
- 6 types: loose, dense,
bone, fat, blood, cartilage
- Muscle
tissue
- Contractile proteins (actin & myosin)
- 3 types: cardiac, smooth, skeletal
- Nervous
tissue
- Organs
- Heart, lung, liver, kidney, skin
- Which organ in your body is the largest?
- Organ systems
- Digestive
- Circulatory
- Respiratory
- Immune
- Excretory
- Endocrine
- Reproductive
- Nervous
- Musculoskeletal
Physiological Principles
Exchange with the environment
"Rate of flow is proportional to surface area"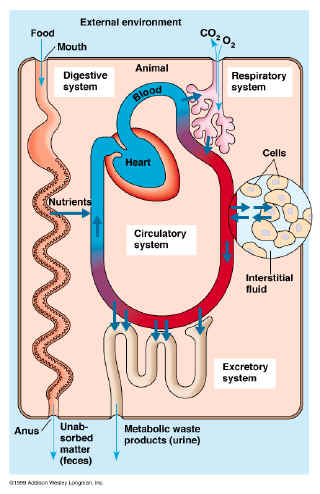
Examples & physiological adaptations
- Respiration: alveoli (300 - 600 million): ~100 m2
- Nutrient absorption: microvilli (>250 m2)
- Circulation: capillaries (6300 m2)
- Filtration of blood: nephrons (2 million) = ~0.3 m2
Examples of homeostasis
- Thermoregulation
- Acid-base balance (pH)
- Osmoregulation (salt/water balance)

